Managing Network Security Groups NSGs and Analyzing Traffic Between Azure Virtual Machines.
This guide covers how to manage Network Security Groups (NSGs) and analyze network traffic between Azure Virtual Machines, focusing on configuring security rules and monitoring data flow to ensure proper access control and network security.

Network Security Groups (NSGs) and Inspecting Traffic Between Azure Virtual Machines
In this tutorial, we observe various network traffic to and from Azure Virtual Machines with Wireshark as well as experiment with Network Security Groups.
Environments and Technologies Used
Microsoft Azure (Virtual Machines)
Remote Desktop
Various Command-Line Tools
Various Network Protocols (SSH, RDH, DNS, HTTP/S, ICMP)
Wireshark (Protocol Analyzer)
Operating Systems Used
Windows 10 (21H2)
Ubuntu Server 20.04
Actions and Observations
Welcome to my tutorial on Network Security Groups and Inspecting Network Protocols. First you will need to create two VMs on Azure. One machine will be a Linux machine and the other will be a Windows 10 machine. Both will have two cpus and they must be on the same VNET. Once that is done go on the Windows machine and download Wireshark. I will attach a link to the Wireshark download. https://www.wireshark.org/download.html Once installed open Wireshark and filter for ICMP Traffic only. ICMP is a network layer protocol that relays messages concerning network connection issues. Ping uses this protocol, ping tests connectivity between hosts. When we filter Wireshark to only capture ICMP packets and ping the private IP address of our Linux machine we can visually see the packets on Wireshark.
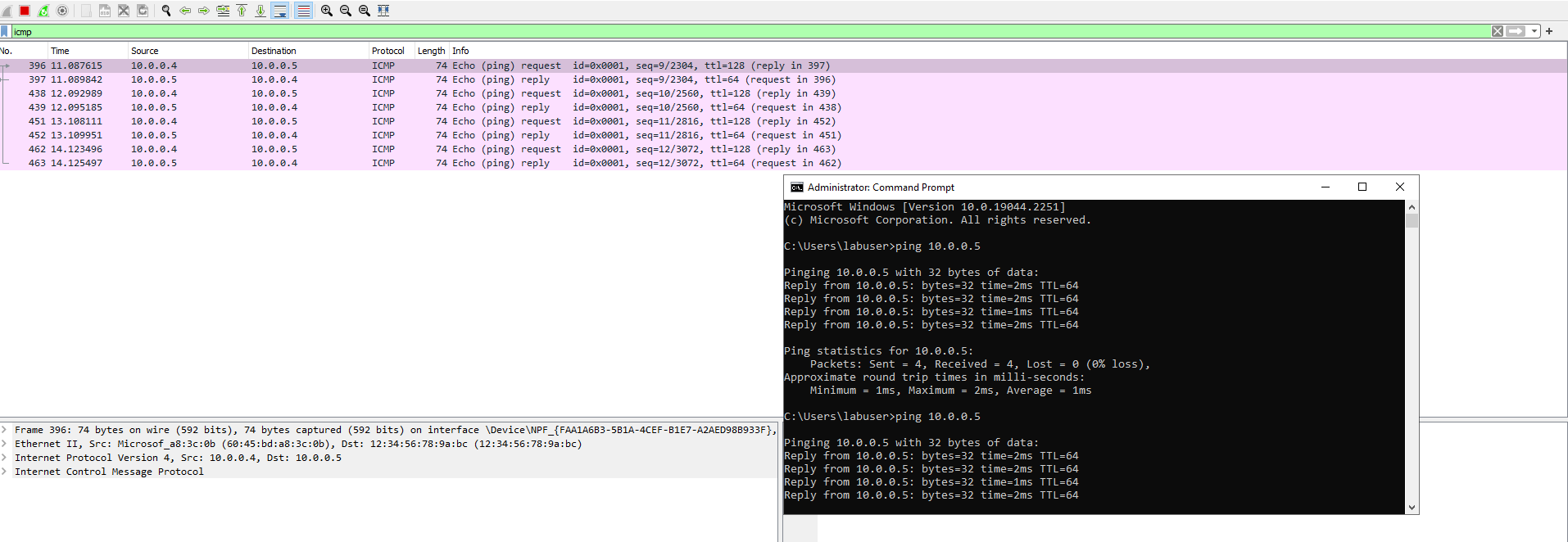
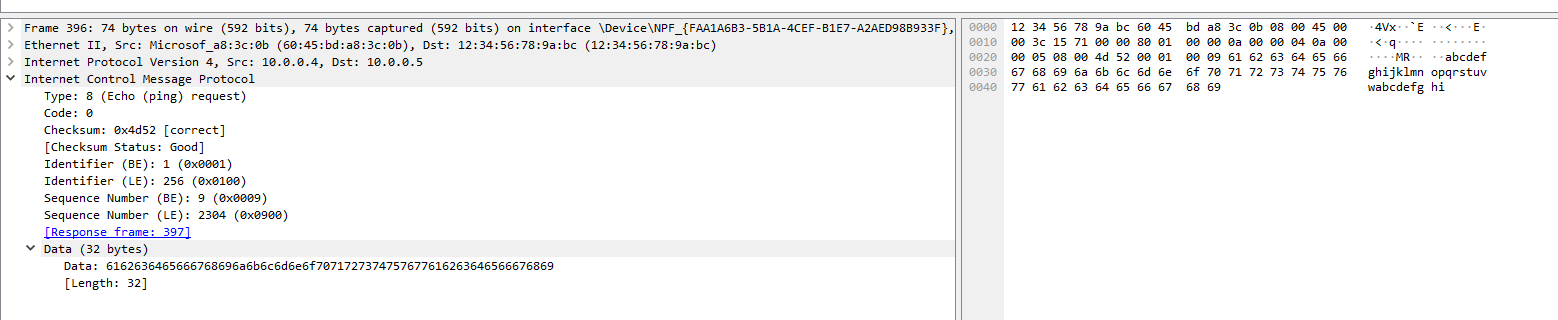
We can inspect each individual packet and see the actual data that is being sent in each ping. the picture below demonstrates just that.
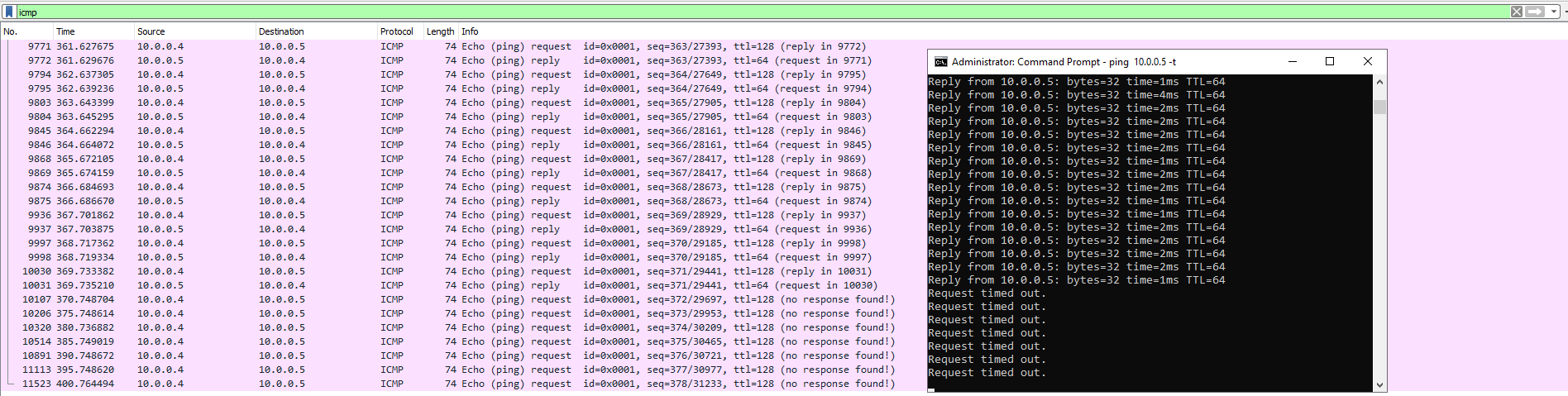
In the next portion of the lab we will perpetually ping the Linux machine with the command ping -t. This will continually ping the machine until we decide to stop it, while the Windows machine is pinging the Linux machine we will go to the Linux machine and block inbound ICMP traffic on it's firewall. Once we do that we will stop receiving echo replies from the Linux machine. We will block ICMP by creating a new Network Security Group on the Linux machine that will be set to block ICMP. We can allow the traffic by allowing ICMP on the Linux Network Security Groups page on Azure.
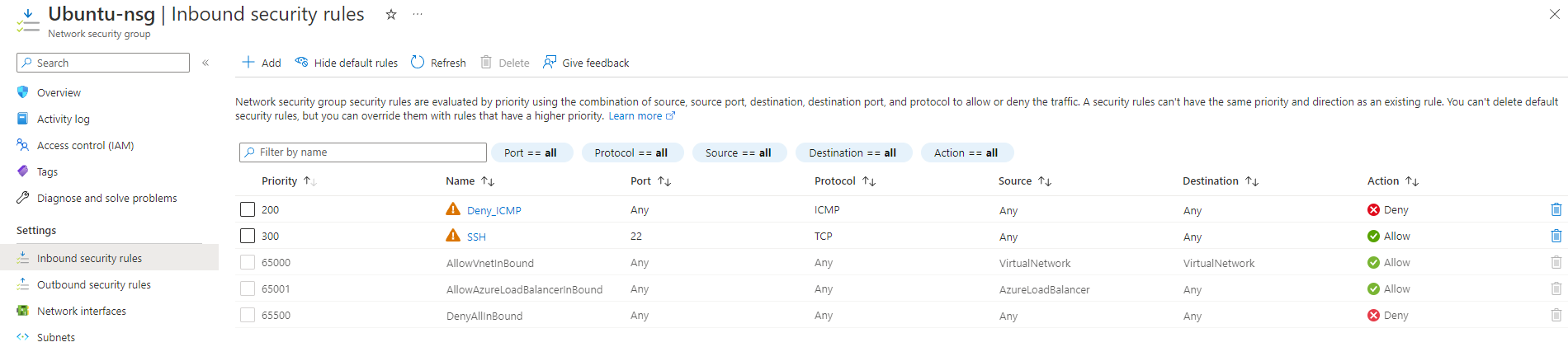
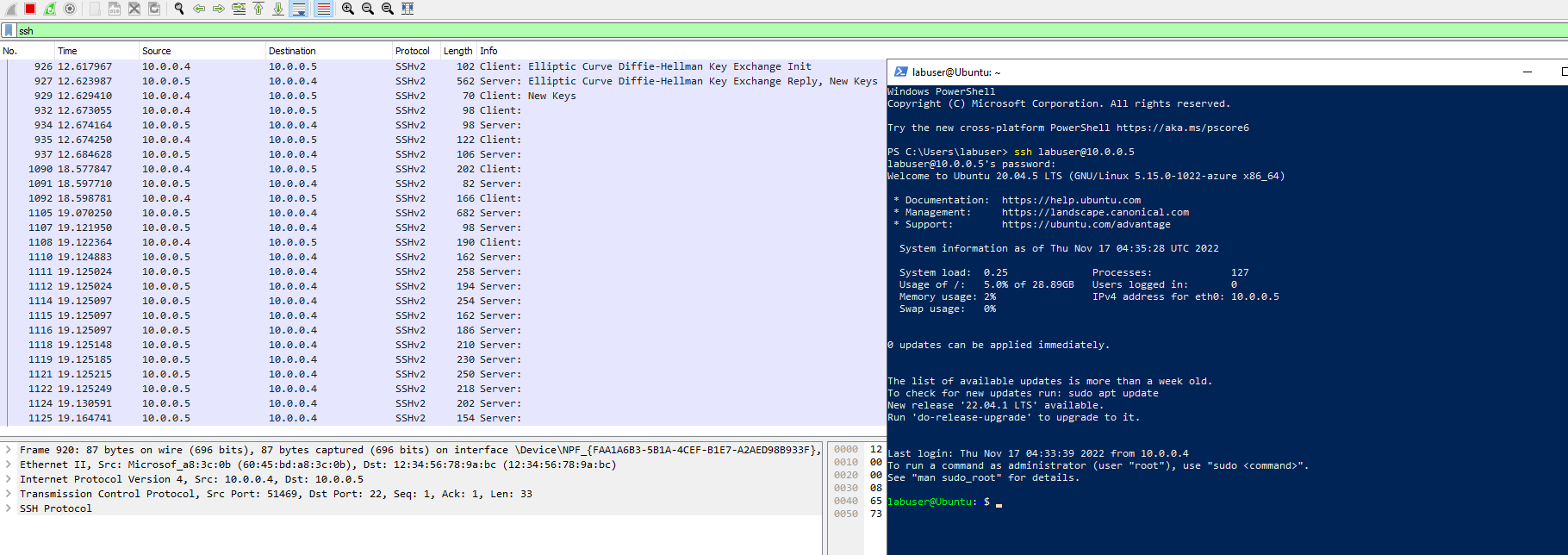
Next we will use our Windows machine to SSH to the Linux machine. SSH has no GUI it just gives the user access to the machines CLI. We will set the Wireshark filter to capture SSH packets only. When we SSH into the Linux machine with the command prompt "SSH [email protected]" we can see that Wireshark starts to immediately capture SSH packets.
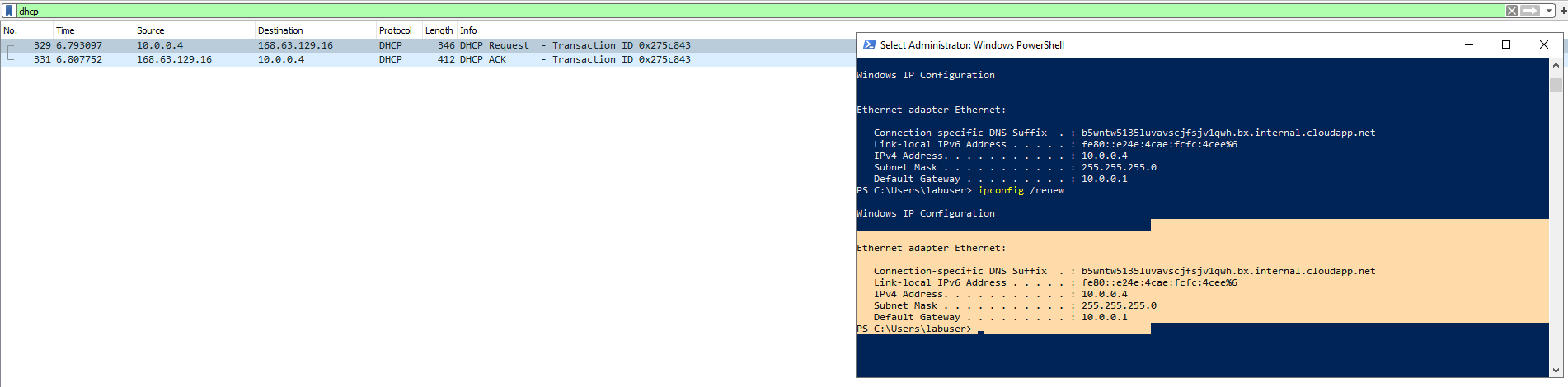
Now we will use Wireshark to filter for DHCP. DHCP is the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol this works on ports 67/68. It is used to assign IP addresses to machines. We will request a new ip address with the command "ipconfig /renew". Once we enter the command Wireshark will capture DHCP traffic.
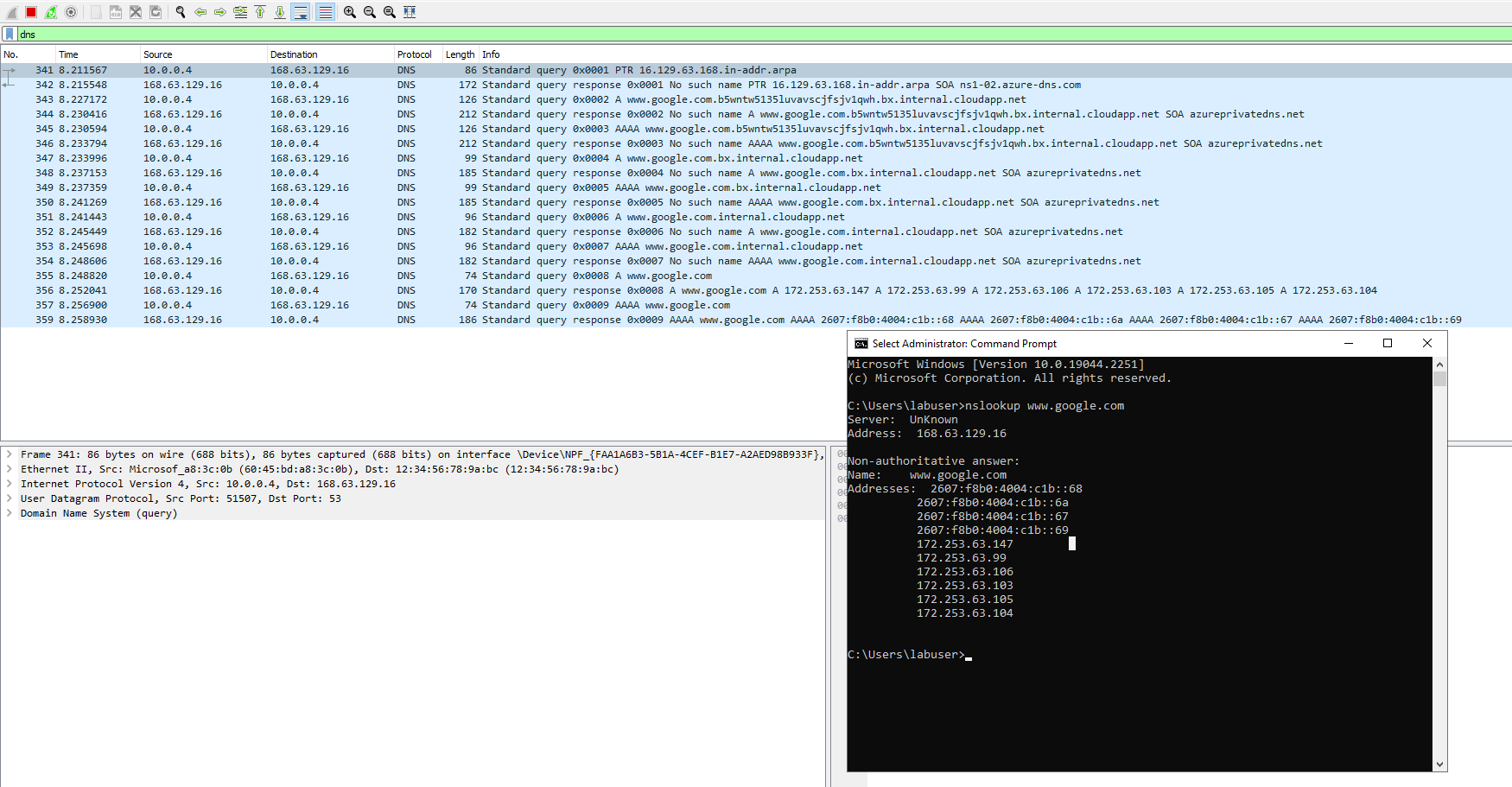
Time to filter DNS traffic. We will set Wireshark to filter DNS traffic. We will initiate DNS traffic by typing in the command "nslookup www.google.com" this command essentially asks our DNS server what is Google's IP address.
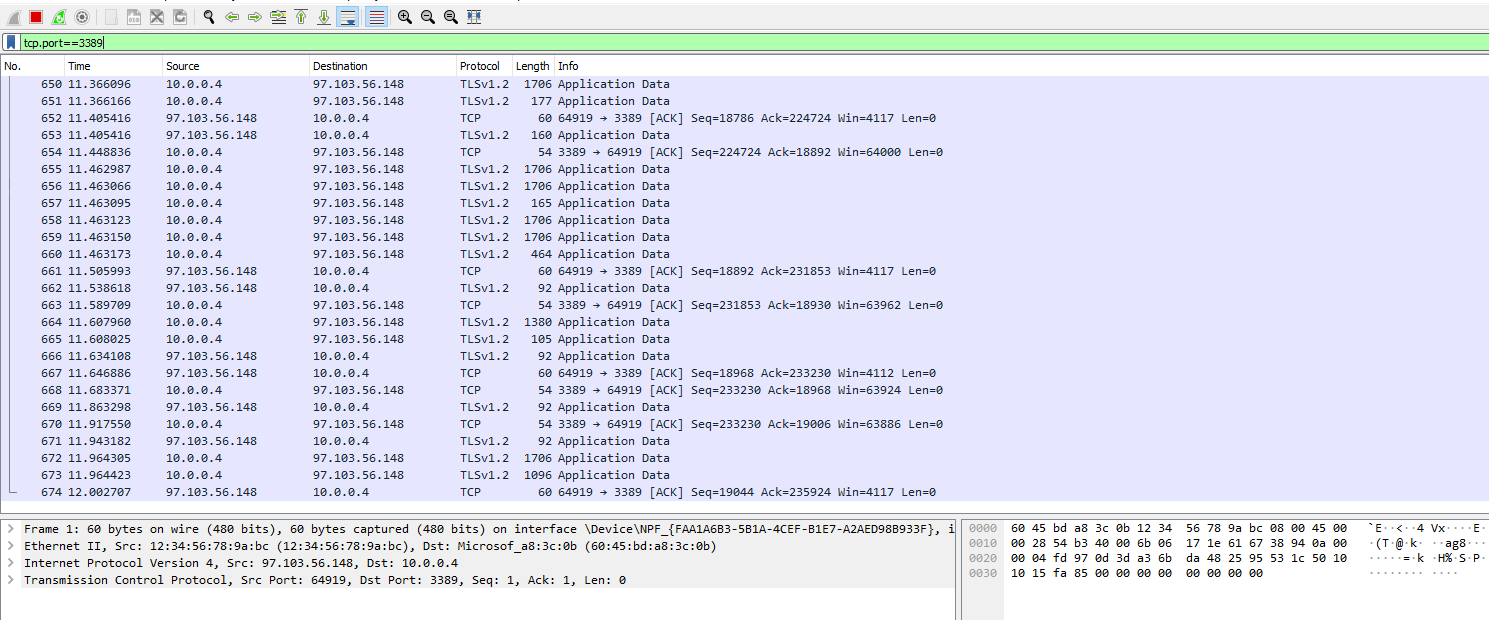
Lastly we will filter for RDP traffic. When we enter tcp.port==3389 traffic is spammed non stop because we are using Remote Desktop Protocol to connect to our Virtual Machine.