Understanding The DHCP Protocol.
March 06, 2025
This guide explains how the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) automatically assigns network settings like IP addresses to devices on a network, streamlining configuration and management.
DHCP Protocol (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol).
DHCP is a network protocol used to automatically assign network settings to devices, such as IP addresses, subnet masks, gateways, and DNS settings. The goal is to simplify network configuration by dynamically allocating IP addresses, rather than manually setting them on each device.
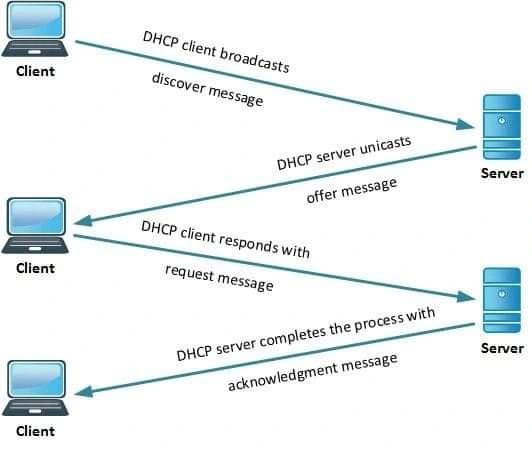
The DHCP process works in the background and involves several steps, which can be observed using network analysis tools like Wireshark. The process follows these six steps:
DHCP Server Setup:
A DHCP server is configured on the network to provide IP addresses and network settings. It has a pool of available IP addresses ready for assignment. The server can run on Windows Server, Linux, or even a router or core switch.
DHCP Discover:
When a device joins the network, it sends a broadcast message called DHCP Discover to search for a DHCP server.
DHCP Offer:
Upon receiving the DHCP Discover message, the DHCP server responds with a DHCP Offer, which includes an available IP address for the device.
DHCP Request:
The device then sends a DHCP Request to the server to confirm its acceptance of the offered IP address.
DHCP Acknowledgment:
The DHCP server sends a DHCP Acknowledgment to confirm the assignment of the IP address to the device.
DHCP Lease:
The IP address is leased to the device for a specific time, known as the DHCP Lease period. Once the lease expires, the device must renew the IP address with the server to maintain the connection.

